- MAP modified atmosphere packaging,It is a packaging technique that extends the shelf life of food by filling a single or mixed gas into a packaging bag or modified atmosphere box. Its main purpose is to ensure that the product is stored, transported, and sold under refrigeration (above 0 degrees Celsius) conditions, ensuring the original color and flavor of the food, just like locking the freshness of the food inside the packaging. Therefore, it is commonly referred to as modified atmosphere lock fresh packaging or modified atmosphere preservation packaging.
According to the different packaging materials, modified atmosphere packaging is usually divided into two categories:
- Soft film inflatable packaging: Typically, external or internal vacuum packaging machines, including vacuum packaging machines and fully automatic stretch film vacuum packaging machines, can be equipped with an inflation function to fill with protective gas to extend the shelf life of food or prevent food from being squeezed.
- Hard box modified atmosphere packaging: Generally, what we refer to as modified atmosphere packaging is hard box modified atmosphere packaging. Put the product into the gas control box, use a vacuum pump to evacuate, extract residual oxygen, then fill it with single or mixed gas, and then heat seal it with a sealing film. So this packaging method is called modified atmosphere sealed box fresh lock packaging.

- Although traditional vacuum packaging can extend the shelf life of food to several months or even 2 years, vacuum packaged food generally needs to be frozen and stored. These post-processing processes determine that vacuum packaging is not suitable for packaging fresh food, such as cold meat, vegetables, fruits, etc.
The main function of modified atmosphere lock fresh packaging is to maintain the respiratory activity of fresh food by adjusting the gas composition structure inside the packaging, inhibit the growth and reproduction of microorganisms, and ensure that the shelf life of food can be extended to 7-15 days under low-temperature refrigeration conditions above 0 degrees Celsius, without changing the basic characteristic of “freshness” of fresh food. It should be clarified that products packaged with modified atmosphere can also undergo high-temperature sterilization and cryopreservation. However, for fresh meat, aquatic products, vegetables, and fruits, the most important significance of modified atmosphere packaging is still preservation in a low-temperature, non freezing environment.
Products packaged in modified atmosphere packaging can showcase the company’s logo and shape brand image through labeling and other means
The extended shelf life of modified atmosphere packaging products can effectively expand the distribution range of fresh products, expand sales areas, increase brand awareness, and increase business revenue and profits for enterprises.
The use of vacuum packaging can effectively reduce food waste and has important social significance.
- Modified atmosphere packaging requires filling a single or mixed gas into the modified atmosphere box. To ensure the quality of modified atmosphere packaging, these gases require extremely high purity, typically reaching 99.99% or higher. Gas is stored in steel cylinders and needs to be equipped with a pressure reducing valve, which is connected to the inflation pipeline of the modified atmosphere packaging machine through a connecting machine. If mixed gas is injected, a gas mixer is also required. Before entering the modified atmosphere packaging machine, the gas is mixed into a specific proportion through the gas mixer.
The most commonly used gases in modified atmosphere packaging are O2, CO2, and N2. We must choose the gas and mixing ratio based on the characteristics of the packaged food. These gases can be used alone or in combination to find the optimal solution and strike a balance between extending the shelf life of food and maintaining its optimal flavor. - Nitrogen (N2)
Nitrogen is an inert gas that does not react with food and has no odor, taste, or color. Nitrogen has a lower density than air, is not flammable, and has low solubility in water (0.018 g/kg at 100 kPa, 20 ° C) and other food ingredients.
Nitrogen can effectively inhibit the growth and reproduction of aerobic microorganisms, thus slowing down the food spoilage caused by it. But nitrogen cannot prevent the growth and reproduction of anaerobic bacteria.
Based on the low solubility of nitrogen in food, we can use it as a filling gas in packaging. By adding sufficient N2 to the gas mixture, we can balance the gas volume reduction caused by CO2’s easy solubility in water, thereby preventing packaging collapse. Packaging collapse is caused by foods containing high moisture and fat, as these foods absorb carbon dioxide from the packaging, resulting in a decrease in gas inside the packaging, a decrease in air pressure, and an imbalance in air pressure inside and outside the packaging, leading to packaging collapse. In MAP packaging of dry snack products, 100% nitrogen is usually filled to prevent oxidation, rancidity, and compression protection. - Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Carbon dioxide is a colorless gas that has a slight irritating odor at very high concentrations. It is a suffocating agent with slight corrosiveness in the presence of water. CO2 is easily soluble in water (1.57 g/kg @ at 100 kPa, 20 ° C) to form carbonic acid (H2CO3), which increases the acidity of the solution and lowers the pH value. This gas is also soluble in lipids and some other organic compounds.
The solubility of CO2 increases with decreasing temperature. Therefore, the antimicrobial activity of CO2 is significantly higher at temperatures below 10 ° C than at temperatures of 15 ° C or higher, which is of great significance for the modified atmosphere packaging of food.
Due to the reduction in volume of the top space, the high solubility of CO2 can cause packaging collapse. This type of packaging needs to be filled with nitrogen for balance.
Carbon dioxide inhibits the growth of most aerobic bacteria. Usually, higher levels of CO2 mean longer shelf life. However, many high moisture and high-fat foods absorb carbon dioxide, and excessive carbon dioxide in modified atmosphere packaging can lead to packaging collapse, flavor contamination, and water loss. Therefore, in industrialized modified atmosphere packaging, the most important thing is to find a balance between the ideal shelf life and the degree of tolerable negative effects. It is recommended to contain at least 20% CO2 in the mixed gas to control bacterial growth. - Oxygen (O2)
Oxygen is a colorless and odorless gas that easily oxidizes with food and supports combustion. Its solubility in water is very low (0.040 g/kg, 100 kPa, 20 ° C).
Oxygen can promote several types of spoilage reactions in food, including fat oxidation, browning, and pigment oxidation. Most common spoilage bacteria and fungi require oxygen to grow. Therefore, to extend the shelf life of food, modified atmosphere packaging should contain low concentrations of residual oxygen.
It should be noted that low concentrations of oxygen in certain foods can lead to quality and safety issues (such as adverse color changes in red meat pigments, aging of fruits and vegetables, and growth of food poisoning bacteria), and these factors must be fully considered when selecting the gas composition of packaged food. Oxygen usually exists in modified atmosphere packaging for sufficient reasons, including maintaining the freshness and natural color of food (i.e. red meat); Maintain breathing of fresh vegetables and fruits; Inhibiting the growth of anaerobic organisms (some vegetables and fish). - Carbon monoxide (CO)
Carbon monoxide is a toxic, colorless, odorless, and flammable gas. In terms of decomposition into carbon and oxygen, it is stable at up to 400 ° C. Research has shown that the use of carbon monoxide (CO) in MAP modified atmosphere packaging containing high concentrations of CO2 can prolong the shelf life and maintain the bright red color of the meat. Please note that CO is not allowed in modified atmosphere packaging in Europe.
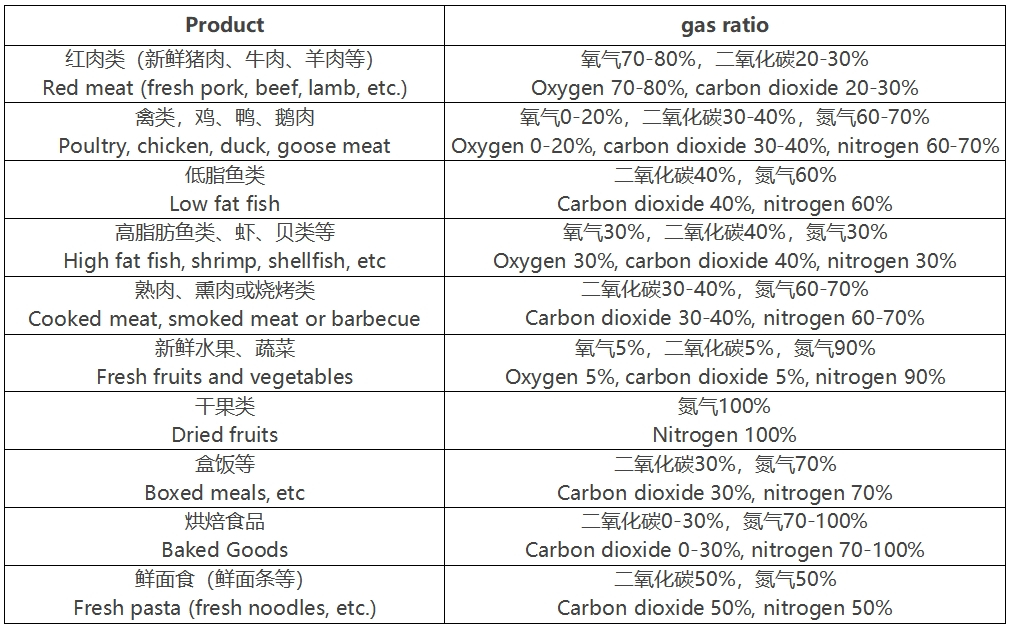
Like other packaging methods, the shelf life of modified atmosphere packaging food is related to the pre-treatment process before packaging, the temperature of food storage and transportation, the purity and residual oxygen content of the gas, the accuracy of gas mixing, the quality level of the modified atmosphere packaging machine, and the characteristics of the food itself.
- The modified atmosphere packaging gases for fresh pork, beef, and lamb are composed of CO2, O2, etc. High concentrations of O2 oxidize myoglobin in meat to oxygenated myoglobin, which can maintain a bright red color in fresh meat; CO2 is used for antibacterial and anti-corrosion purposes. The shelf life under 0-4 ℃ conditions is 7-30 days.
Fresh poultry can be kept fresh using gases such as CO2 and N2, with a shelf life of 15-30 days at 0-4 ℃ and 2-5 days at room temperature.
- After packaging, intact or sliced fruits and vegetables still maintain their metabolic and respiratory activities of absorbing O2 and excreting CO2. If the O2 content inside the packaging decreases and the CO2 content increases, it can maintain weak aerobic respiration in fruits and vegetables without anaerobic respiration, reduce metabolic rate, and thus extend the shelf life.The modified atmosphere packaging freshness gas for fresh fruits and vegetables is composed of O2, CO2, and N2.
- The freshness period of modified atmosphere packaging is determined based on the variety and freshness of fruits and vegetables, such as strawberries, mushrooms, lychees, peaches, leafy vegetables, etc. The shelf life at 0-4 ℃ is 10-30 days. Using a low resistance diaphragm.
- The modified atmosphere packaging of Chinese and Western style livestock and poultry cooked food products, braised vegetables, stir fried vegetables, stewed vegetables, fast food boxed meals and other cooked food products requires preservation, preservation and preservation of the original flavor. The preservation gas is generally composed of CO2, N2 and other gases. After modified atmosphere packaging, the preservation gas forms a protective film on the surface of the food, thereby achieving the purpose of antibacterial preservation, maintaining the nutritional content, original taste, flavor, and shape of the food.
- Shelf life below 20 ℃ for 5-10 days or more; Under the condition of 0-4 ℃, the shelf life is 30-60 days; After using pasteurization (around 80 ℃), the shelf life at room temperature is above 60-90 days. High resistance diaphragm is required.
- The spoilage of baked goods is mainly caused by mold, so the purpose of modified atmosphere packaging is to prevent mold and maintain flavor. The preservation gas is composed of CO2 and N2. After being packaged with modified atmosphere, the shelf life of rice noodles such as cakes and bread at room temperature is 15-60 days; The shelf life of mooncakes at room temperature is 30-90 days. The packaging film needs to use composite plastic film with high gas barrier properties to maintain the gas concentration inside the packaging.
- Fresh fish and shrimp and other aquatic products are perishable foods with high moisture content. Anaerobic bacteria are one of the factors causing spoilage of fresh aquatic products during low-temperature storage, and they produce toxins that are harmful to human health. The preservation gas is composed of O2, CO2, and N2.
- The modified atmosphere packaging of fatty fish is mainly due to the fact that fatty acids are the main factors causing spoilage, and the protective gas is composed of CO2 and N2.
- The modified atmosphere packaging of fresh aquatic products has a shelf life of 15-30 days at a temperature of 0-4 ℃, depending on the variety and freshness. The packaging film needs to use composite plastic film with high gas barrier properties to maintain the gas concentration inside the packaging.
- Pickled vegetables are prone to oxidation, mold and spoilage in the air. During the pickling process, an appropriate amount of natural biological agents are added, and after being packaged with modified atmosphere, they can be preserved for 30-180 days at room temperature. The preservation gas is composed of CO2 and N2.







